How Much Does a Home Extension Costs?
Adding extra space to your home can completely change how comfortable and functional it feels.
But before you move forward, it’s important to understand the real cost involved.
The price of a home extension can vary widely depending on the type of space, materials, labor, and where you live.
From small bump-outs to full second-story builds, the expenses can add up fast if you’re not prepared.
This guide clearly shows how much a home extension costs. It also shares practical tips to help you stay within your budget and make smart choices from the start.
If you’re planning to expand, this is the place to begin with confidence.
Average Cost of a Home Extension
The cost of a home extension typically ranges from $150 to $450 per square foot. Most homeowners spend between $40,000 and $140,000 on their projects.
Cost by Square Feet
| Size (Square Feet) | Basic Quality | Medium Quality | High Quality |
|---|---|---|---|
| 200 | $30,000-$50,000 | $50,000-$70,000 | $70,000-$90,000 |
| 400 | $60,000-$100,000 | $100,000-$140,000 | $140,000-$180,000 |
| 600 | $90,000-$150,000 | $150,000-$210,000 | $210,000-$270,000 |
| 800 | $120,000-$200,000 | $200,000-$280,000 | $280,000-$360,000 |
Examples of Different Budget Extension

A low-end home extension might cost around $40,000. This typically includes a basic 250 sq ft bedroom with no major upgrades.
Standard materials are used, and the homeowner may complete some tasks on their own to help lower labor costs.
A mid-range project averages around $90,000. This could cover a 400 sq ft family room with solid finishes, better-quality windows, and proper heating and cooling systems. It strikes a balance between comfort and value.
A high-end extension usually starts at $175,000 or more. This might include a kitchen or large living space over 500 sq ft with top-tier materials, custom features, and advanced appliances or fixtures.
These upgrades contribute to a higher final price but bring long-term function and comfort.
Home addition Costs by Room Type
| Room Type | Cost Range | Price Per Sq Ft | Key Cost Factors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bedroom | $35,000-$80,000 | $100-$200 | Closets, windows, HVAC |
| Bathroom | $40,000-$100,000 | $250-$450 | Plumbing, fixtures, waterproofing |
| Kitchen | $65,000-$150,000 | $300-$500 | Appliances, cabinets, plumbing |
| Home Office | $30,000-$75,000 | $100-$250 | Electrical, built-ins, lighting |
| Second Story | $100,000-$300,000+ | $300-$500 | Structural support, stairs, roof work |
Key Factors that Affect Cost
Several factors can affect the cost of a home extension. These include the type of room, its size, materials, labor, and local regulations.
Costs may also increase if the layout of your current home needs adjustments before building.
Seasonal timing and demand for contractors in your area can affect pricing, too.
1. Type and Size of the Extension
The bigger your extension, the more it will cost. But size isn’t the only thing that matters. Some types of rooms cost more than others because they need special features.
A simple bedroom might cost $100-$200 per square foot, while a bathroom or kitchen with plumbing and special fixtures might run $250-$450 per square foot.
2. Materials Used
The materials you choose can make a big difference in overall cost.
Vinyl siding typically costs $5 to $10 per square foot, while brick can cost $15 to $30 per square foot.
Flooring also varies—laminate is more budget-friendly at $3 to $7 per square foot, compared to hardwood, which ranges from $10 to $25 per square foot.
Window prices depend on the type you select: standard models usually cost $300 to $700 each, while energy-efficient options range from $800 to $1,200.
For roofing, asphalt shingles cost $3 to $5 per square foot, while metal roofing can cost up to $10 to $20 per square foot.
3. Labor and Contractor Rates
In this year, labor typically makes up 30-50% of your total project cost. Contractor rates vary by:
In urban areas, the overall cost of a home extension can be 15% to 20% higher compared to rural regions. This increase is often due to higher labor charges, permit fees, and material costs.
The time of year also plays a role—contractors tend to raise rates during peak summer months when demand is high.
Hiring specialists like electricians or plumbers with advanced skills usually results in higher hourly rates than hiring general contractors.
These factors combined can significantly influence the final budget of a home extension project.
4. Location and Site Conditions
Where you live can influence the total cost in a few important ways.
Prices in the Northeast and West Coast are often 20 to 30 percent higher than in the Midwest or South.
Local building codes may also require extra safety features or inspections, which can raise costs.
In extension, the condition of your land plays a role. Sloped lots, poor soil, or areas with limited access can increase your expenses by 10 to 25 percent due to the extra work needed.
5. Permit and Zoning Requirements
Before construction starts, you’ll need to account for important paperwork and approval fees.
Building permits can cost anywhere from $500 to $2,000, depending on your area and the size of the project.
Inspection fees usually range between $100 and $500 each time an inspector visits the site.
If your design requires official drawings, architectural plans may cost between $2,000 and $8,000. You might also need a property survey, which typically falls between $300 and $800.
In some areas, local rules are strict, and getting special approval (known as a variance) could add another $500 to $3,000 to your total.
These steps are essential for meeting rules and making sure the extension is approved.
Pros and Cons of Each Room Type
When planning your home extension, the room type you choose can greatly impact the overall cost and complexity.
For example, adding a bedroom may be a straightforward project, but including a bathroom or kitchen could significantly increase the price due to plumbing and appliance installations.
Bedroom extension
A bedroom extension is a great way to add value to your home without much complexity. It’s one of the more affordable and straightforward extensions, making it a solid choice for increasing living space.
However, while it adds value, it may not offer as much resale value as other extensions like kitchens or bathrooms.
Bathroom extension
Adding a bathroom is a practical and high-return investment, as it is essential for modern living and increases home value.
On the downside, bathroom extensions can be expensive due to the complexity of plumbing and other installations.
The cost per square foot for a bathroom extension is also higher than for many other types of room expansions.
Kitchen extension
A kitchen extension is often considered one of the best ways to boost a home’s value and improve day-to-day life.
A more spacious kitchen can be a game-changer for a home.
However, it’s also one of the most expensive and complex types of extensions, involving significant work, materials, and planning.
Home Office extension
As remote work continues to rise, a home office extension is becoming increasingly valuable. It’s one of the least expensive extensions and is ideal for those looking to optimize their home for working from home.
However, depending on your area’s real estate market, it might need to be converted back to a bedroom when reselling, which could limit its appeal.
Second Story Addition
A second-story addition can double your living space without expanding your home’s footprint, which is especially beneficial if you’re limited by lot size.
This type of extension is more complex, requiring significant structural work, and can often involve temporarily relocating, which adds to its complexity.
Building Out vs. Building Up
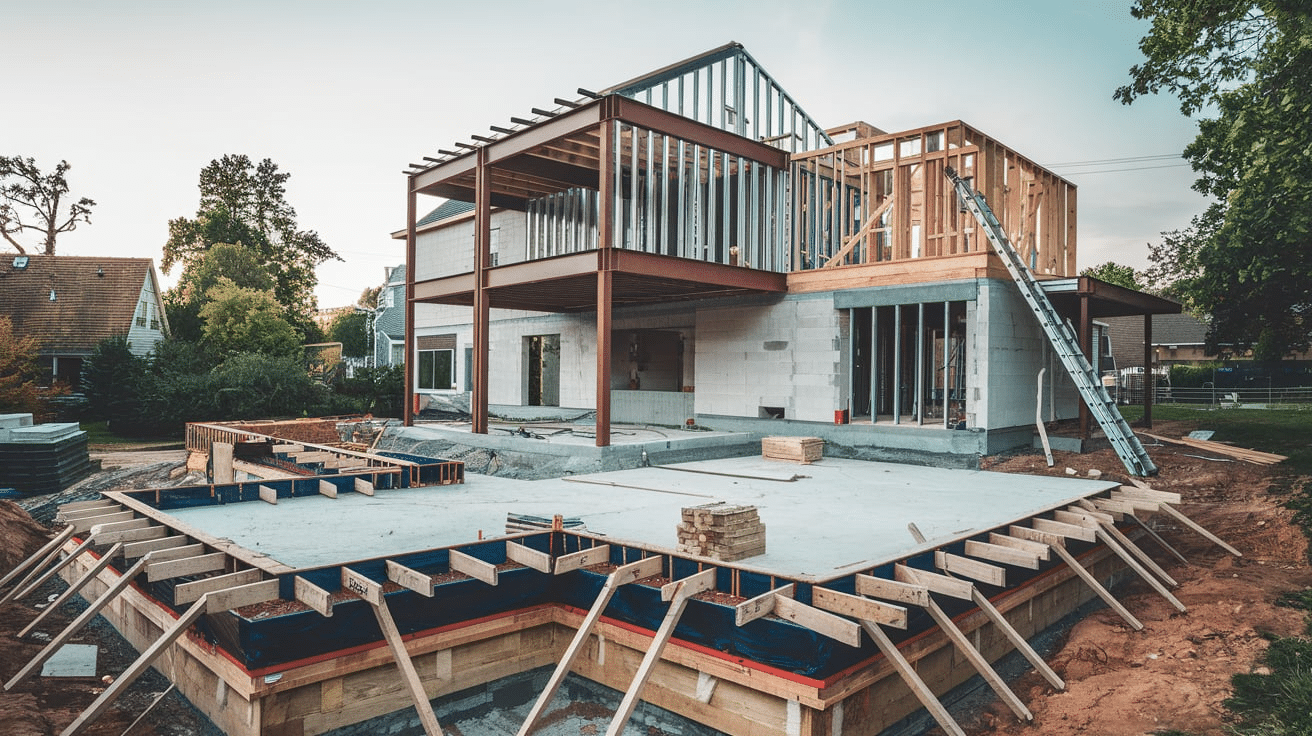
When adding space, you have two main options: extending outward or adding a second floor.
Building out (a horizontal extension) typically costs between $150 and $300 per square foot. This type of extension requires a new foundation, exterior walls, and an extension to the roof.
It generally takes around 2 to 4 months to complete, depending on the complexity of the project and any site-specific conditions.
On the other hand, building up (a vertical extension) costs between $300 and $500 per square foot. This option involves structural reinforcement, the installation of stairs, and sometimes the removal and replacement of the roof.
The timeline for a vertical extension is usually longer, taking around 3 to 6 months to finish due to the extensional steps required for safety and structural stability.
Foundation vs. Roofing Considerations
Foundation for Building Out: When adding space to your home by building out, a new foundation is required, which can cost between $5,000 and $25,000.
Depending on the location and soil conditions, soil testing may also be needed, with prices ranging from $500 to $3,000.
Excavation work, which includes clearing the area and preparing it for the foundation, typically costs between $2,000 and $8,000.
Roof Work for Building Up: Building upward requires extensional roof work.
First, the existing roof must be removed, which can cost anywhere from $2,000 to $10,000. To support the new structure, structural reinforcement is often necessary, with costs ranging from $10,000 to $30,000.
Finally, a new roof must be installed, which can cost between $8,000 and $20,000, depending on the materials and complexity.
Which is Better for Different Homes?
The right choice often depends on your home’s size, layout, and daily needs. Some homes work better with compact features, while others benefit from wider setups.
It also helps to consider how much natural light your space gets. Your personal habits and how you use each room can also help determine the best option.
| Building Out Works Best For: | Building Up Works Best For: |
|---|---|
| Single-story homes | Homes on small lots |
| Homes on large lots | When local zoning restricts horizontal expansion |
| When you want to avoid major disruption to existing living spaces | When you want to maintain yard space |
How to Save on Your Home Addition

One of the best ways to save on your home addition is by considering using less expensive materials.
Opting for prefabricated options or synthetic materials can significantly lower costs while still providing a high-quality finish.
Additionally, tackling some of the finishing work yourself, such as painting or installing fixtures, can further reduce your expenses.
Use Alternative Materials
Opt for vinyl plank instead of hardwood flooring, which can save you $7 to $15 per square foot.
Choose quartz countertops instead of marble, saving $20 to $40 per square foot.
Select fiberglass doors rather than solid wood, saving anywhere from $500 to $1,000 per door.
Convert Existing Spaces
Sometimes, the most affordable way to add space isn’t to build an extension at all.
Finishing a basement can cost between $25 and $50 per square foot, while converting an attic might range from $50 to $150 per square foot.
Enclosing a porch, on the other hand, can cost anywhere from $100 to $200 per square foot.
However, these options can be 30-60% less expensive than constructing a new space.
Take On DIY Tasks
Sometimes, the most affordable option isn’t adding new space at all.
Finishing a basement can cost $25 to $50 per square foot while converting an attic ranges from $50 to $150 per square foot.
Enclosing a porch is another cost-effective solution, typically costing between $100 and $200 per square foot.
These alternatives can be 30-60% cheaper than building new space, making them an excellent option for homeowners looking to save money while adding usable space to their homes.
Look for Rebates or Incentives
There are several money-saving opportunities available when considering a home addition.
Homeowners can take advantage of energy-efficient tax credits, which can be up to $2,000.
Additionally, local home improvement grants vary depending on location, offering more personalized support.
Many utility companies provide rebates for incorporating energy-saving features into your project.
For eligible homeowners, low-income home improvement assistance programs can help make improvements more affordable.
Step-by-Step Budgeting Guide
- To begin, define your needs and wants clearly. Identify the essential features for your home addition and distinguish them from the nice-to-haves.
- Next, calculate the square footage of your intended addition by multiplying the length by the width to get a rough estimate of space.
- Once you’ve outlined the scope, research local costs by talking to 3-5 contractors for quotes so you can compare different offers.
- After that, add up the material costs by obtaining quotes from suppliers for major items like roofing, flooring, or plumbing.
- Finally, don’t forget to factor in design costs. Set aside 3-8% of the total budget for architectural plans to ensure your project meets all requirements.
Planning for Unexpected Costs
Set aside a contingency fund:
- 15-20% for extensions to older homes (pre-1980)
- 10-15% for extensions to newer homes
- 5-10% for simple, low-complexity projects
Common surprise costs include:
- Finding outdated wiring or plumbing: $2,000-$15,000
- Discovering mold or rot: $500-$7,000
- Needing foundation reinforcement: $5,000-$25,000
- Code compliance upgrades: $1,000-$10,000
Creating a Financing Strategy
- Check your credit score: Higher scores mean better loan rates
- Calculate how much you can afford monthly: Use the 28/36 rule (housing costs shouldn’t exceed 28% of income)
- Shop for pre-approval: Compare at least 3 lenders
- Consider a payment schedule: It should match the construction phases
Final Thoughts
When planning a home addition, it’s important to assess the costs involved carefully.
Depending on the size, type, and materials used, the price of a home extension can range from $150 to $450 per square foot.
To ensure a smooth process, set a clear budget, get multiple quotes from contractors, and consider the impact of local regulations.
By opting for cost-effective choices like using alternative materials or repurposing existing spaces, you can manage expenses effectively.
A thoughtful approach, with professional guidance, will help ensure that your home extension adds both value and comfort to your home.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Much Does it Cost to Add a Room to Your House?
Adding a basic room typically costs between $35,000 and $80,000. The price depends on size, type, and material quality.
Is it Cheaper to Add On or Build Up?
Adding horizontally (building out) is usually cheaper. Vertical additions (second stories) cost more due to structural work.
What is the Cheapest Way to Add Space to a House?
Finishing a basement, converting an attic, or enclosing a porch or garage are affordable options.
Does Adding a Room Increase Property Value?
Yes, it can increase property value. Depending on the market, most room extensions return 60-80% of their cost.