Top Solar Energy Myths Debunked
In the journey towards a greener planet, solar energy is a beacon of hope, illuminating the path to sustainable living. Yet, amidst its growing popularity, misconceptions cloud its potential, casting shadows of doubt on its efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and environmental impact.
From questioning its ability to power our homes around the clock to underestimating its performance in less sunny locales, these myths often deter individuals from embracing solar solutions. This article aims to clear the air, offering a deep dive into the realities of solar energy.
By exploring its actual efficiency, debunking cost myths, assessing its round-the-clock reliability, examining its environmental footprint, and revealing the surprising durability of solar systems, we aim to provide valuable insights that shine a light on the facts, empowering you to make informed decisions about harnessing the sun’s power.
Exploring the Truth: Is Solar Power Inefficient?

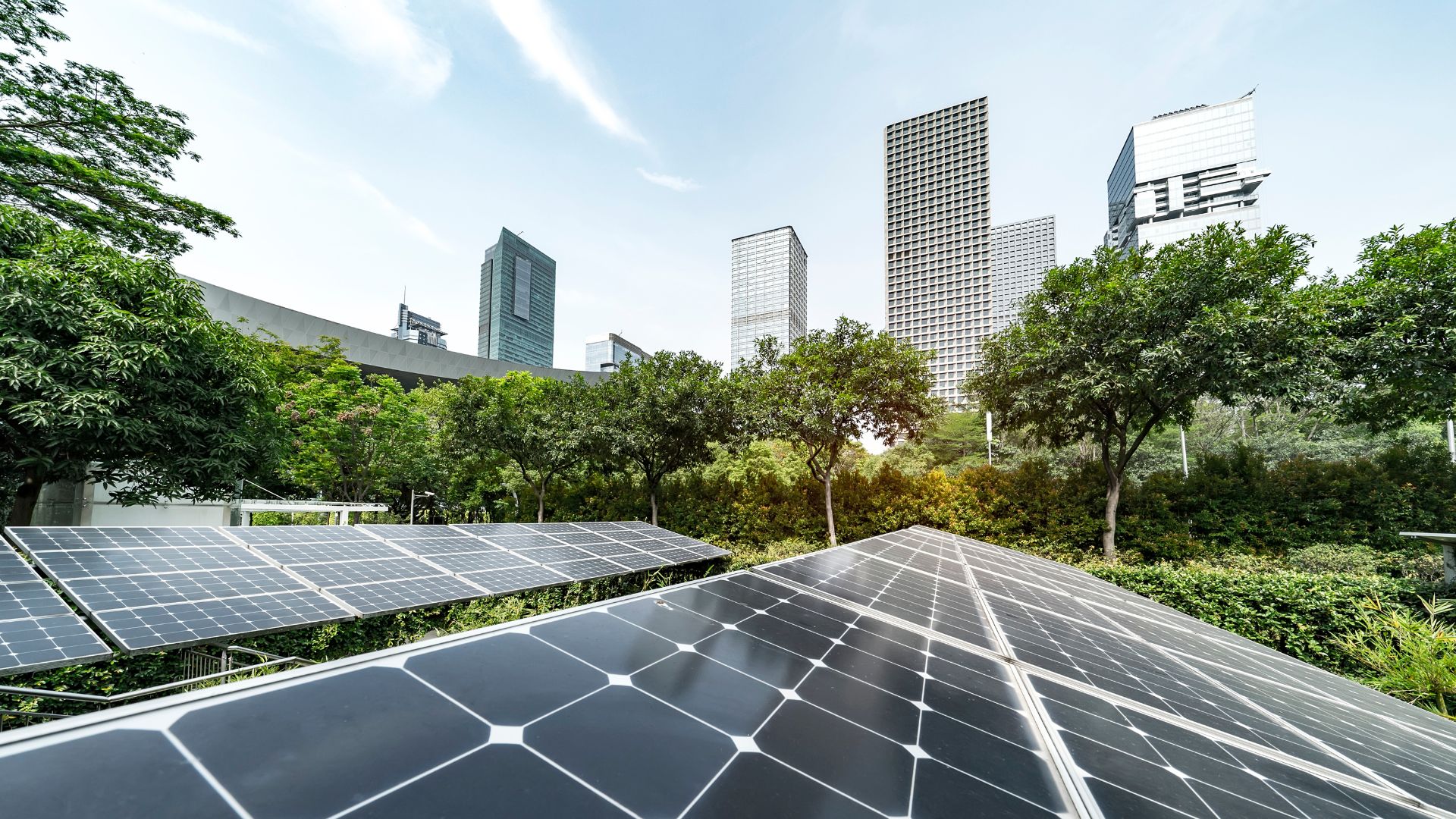
Experts at Sun Valley Solar Solutions say that the efficiency of solar panels has seen significant improvements over the years, with modern photovoltaic (PV) cells capable of converting more sunlight into electricity than ever before. Experts argue that inefficiency stems from early technology and outdated information.
Today’s solar panels, especially those equipped with tracking systems to follow the sun, can achieve efficiency rates of over 20%, which continues to climb as technology advances.
Moreover, the efficiency of solar energy must also be considered in terms of its environmental impact and the ability to reduce carbon footprints, making it a highly effective solution for sustainable energy needs.
Industry professionals emphasize the importance of understanding the broader context of solar energy’s efficiency. For instance, integrating solar power into the grid has become more sophisticated, allowing for better energy supply and demand management.
This enhances the overall efficiency of the power grid and increases the reliability of solar energy as a significant power source. Additionally, advancements in energy storage technology, such as batteries, make solar power more viable than ever, ensuring that the energy produced during the day can be stored and used when sunlight is unavailable.
These developments highlight the ongoing progress in making solar energy a cornerstone of global energy strategies.
Busting the Cost Myth: The Real Expense of Solar Energy
Many potential solar energy users hesitate, fearing the upfront costs are too steep. However, the initial investment in solar technology has significantly decreased over the years, making it more accessible than ever. Experts advise looking beyond the initial price tag and considering the long-term savings.
Solar energy systems can dramatically reduce electricity bills, and with various government incentives and rebates, the effective cost is much lower. Furthermore, the increase in property value and the potential for selling back excess power to the grid means solar installations can benefit financially in the long run.
Experts highlight the importance of understanding the complete financial picture when considering solar energy. The cost of solar panels and installation is only part of the equation. Maintenance costs are relatively low, and the lifespan of a solar power system can exceed 25 years, ensuring long-term savings.
Additionally, as technology advances, the efficiency of solar panels continues to improve, further reducing the cost per watt of solar-generated electricity. With these factors in mind, the actual expense of solar energy is often much lower than perceived, making it an economically viable option for many homeowners and businesses.
Shedding Light on Solar: Can It Power Our Homes 24/7?

The question of whether solar energy can power our homes around the clock is met with skepticism by some. Yet, advancements in technology and energy storage are paving the way for a more resilient and sustainable energy future.
The key to unlocking this potential lies in efficient solar panels and innovative battery storage systems. These technologies have seen significant improvements, enabling the capture of solar energy during daylight and its storage during nighttime or cloudy days. This progress is crucial for solar energy to become a reliable 24/7 power source for residential use.
One of the pivotal components in this equation is integrating intelligent grid technology. Smart grids allow for the more dynamic management of energy resources, balancing supply and demand and more effectively integrating renewable sources like solar power.
This means that even when individual solar panels are not producing electricity, the grid can redistribute energy from stored reserves or other connected renewable sources, ensuring a constant energy supply. The adaptability of smart grids exemplifies how solar energy, when combined with the proper infrastructure, can meet our homes’ energy needs continuously.
The conclusion that solar energy can power our homes 24/7 is becoming increasingly attainable. With the ongoing advancements in solar panel efficiency, battery storage capabilities, and smart grid technology, the foundation for a solar-powered future is stronger.
This shift represents a move towards greater energy independence and a significant step in reducing our carbon footprint and combating climate change. As these technologies evolve and scale, the vision of a solar-powered round-the-clock energy solution is moving from a distant dream to an imminent reality.
The Environmental Impact: Debunking Myths Around Solar Waste
Concerns about the environmental impact of solar energy, particularly regarding solar waste, have circulated widely, yet they often need more context and understanding of the industry’s advancements. Solar panels have a lifespan of 25 to 30 years, after which they can be recycled, mitigating much of the waste concerns.
Recycling processes for solar panels are continually improving, with companies reclaiming over 90% of the materials used in panels, including glass, silicon, and metals like silver and aluminum. This significantly reduces the environmental footprint of solar energy.
Moreover, the energy payback time a solar panel takes to generate the energy used in its production—is typically less than three years, further underscoring solar power’s efficiency and sustainability.
The myth of solar energy contributing significantly to hazardous waste is thus largely unfounded, overshadowed by the technology’s benefits in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and providing clean, renewable energy.
The focus should instead be on supporting and enhancing recycling practices and technological innovations that minimize waste and maximize the environmental benefits of solar energy.
Solar Panels in Cloudy Weather: Fact vs. Fiction
One of the most pervasive myths surrounding solar energy is that solar panels become ineffective in cloudy weather. This misconception stems from a misunderstanding of how solar panels operate. Solar panels can still generate electricity on cloudy days, albeit at a reduced efficiency.
A study by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) found that solar systems could operate at 10% to 25% of their usual output under heavy cloud cover, depending on the panel type. This demonstrates that while there is a decrease in efficiency, the panels do not stop producing electricity altogether.
Additionally, the development of more sensitive photovoltaic materials means that today’s panels are better at converting lower levels of sunlight into electricity.
These technological improvements are crucial for maximizing the potential of solar energy in regions with frequent cloudy weather, making solar a reliable source of green energy even in less sunny locales.
Longevity and Maintenance: The Surprising Durability of Solar Systems
Exploring the durability and maintenance needs of solar energy systems reveals a surprising level of resilience, challenging the myth that they are fragile and high-maintenance.
Solar panels, for instance, are designed to withstand harsh weather conditions, including heavy rain, snow, and even hail, with many manufacturers guaranteeing their performance for 25 to 30 years.