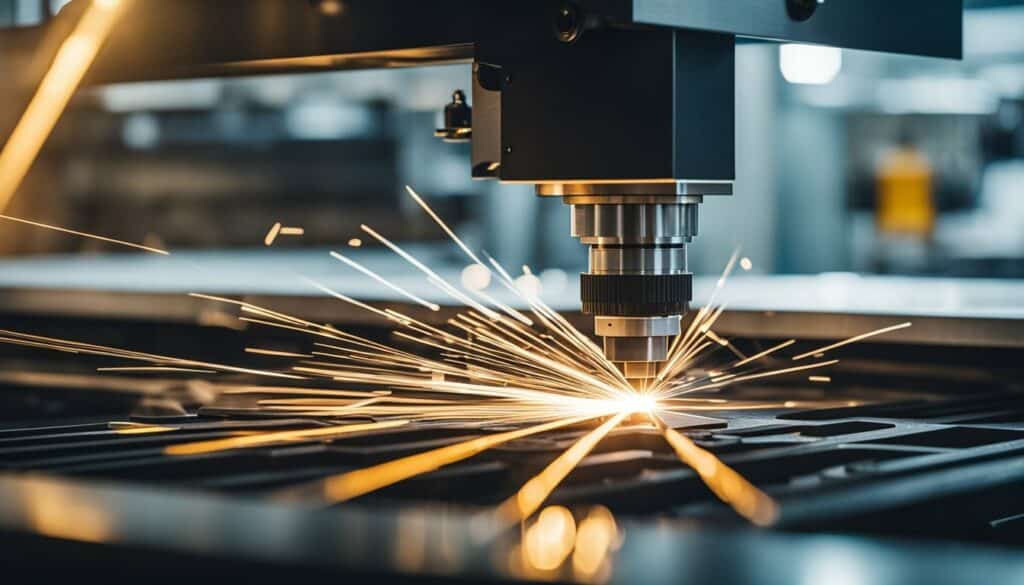
Thinking about how to create your first prototype souvenir or e-bike? Consider how laser cutting – the amplification of light using stimulated emission of radiation — is revolutionizing the manufacturing process prototypes. This technology allows materials of varying thickness and complexity to be processed quickly and accurately using a powerful laser beam.
It used to take weeks to produce complex prototypes, be they machine parts or decorative elements. Now, however, such tasks can be completed in just a few hours. Companies specializing in digital technology, such as Art4youSpace, can convert your drawings into laser SVG files. These files are then used by cutting plotters to turn your prototype into reality.
Notice:
The global market for laser cutting machines, not just products created using laser cutting, is estimated to be worth $5.59 billion in 2023. This market promises to grow to $11.32 billion by 2030 (according to Fortune Business Insights).
Beginning entrepreneurs and prototypers may be frightened — laser cutting is a complicated and expensive venture, but the experience of small companies that are already using this technique to enter the souvenir and accessories market demonstrates their acceptability.
As an alternative, you can consider other prototyping methods (like FDM/FFF, SLA, SLS, MJP/MJM), merely they lose out in speed and quality to laser cutting. This allows you to test the functionality and design of the product before final production.
Manufacturing experts agree: laser shaping undoubtedly speeds up the development of new products and simplifies the process of creating them. Thus, laser technology expands the frontiers for innovation and efficiency in a wide range of industries. Let’s talk about it in more detail.
Advantages of Laser Cutting in Prototyping
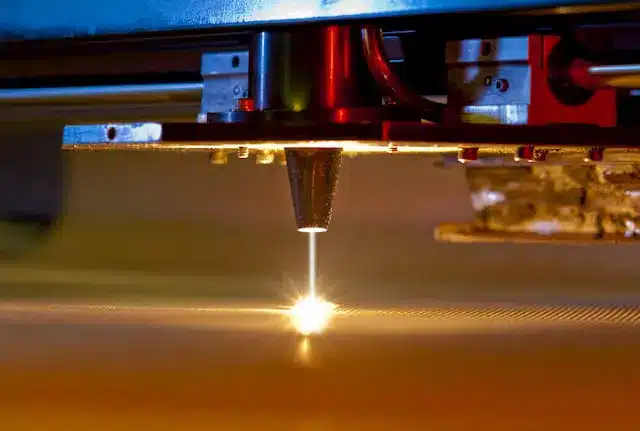 Lazer cutting is a relatively innovative technique that has transformed the prototyping process. From the days of the industrial revolution (think hand saws) and gas cutting, we’ve come a long way to embrace laser cutting, over 100 years.
Lazer cutting is a relatively innovative technique that has transformed the prototyping process. From the days of the industrial revolution (think hand saws) and gas cutting, we’ve come a long way to embrace laser cutting, over 100 years.
This method empowers designers with the speed and precision necessary to breathe life into their ideas, especially when tackling complex projects. Moreover, it drastically reduces design time and minimizes waste, making the entire process more efficient and environmentally friendly.
Benefits of Laser Cutting for Prototyping:
- Precision and detail
- Speed
- Flexibility
- Minimizing waste.
- Ease of use
Technology such as laser cutting is often combined with other technologies to improve efficiency. For example, it can be complemented with laser stereolithography or selective laser sintering.
Start-ups can be inspired by successful examples, such as the use of laser cutting in the automotive industry to create panoramic sunroofs at Mercedes-Benz and side welding at Volkswagen and Audi, and in the aerospace industry to process titanium (Laser Systems). These examples clearly demonstrate the possibilities of precision-cut technology.
The advantages offered by technological innovation in general show that lazer cutting is becoming a key element in speeding up the development of new products and simplifying the process of creating them.
Where once prototyping could take weeks or months, the process now takes days. ASME emphasizes the role of lasers in creating fine features and achieving tight tolerances in manufacturing processes.
Examples of Lazer Cutting Application
In the world of industry, lazer cutting is used to realize the most daring projects, whether it’s creating spare parts for cars or parts for the fashion industry to create accessories. This technology is versatile: metals, plastics, glass — the lazer can easily handle any material, like an artist mastering all the colors of the palette.
| Industry sector | Cutting material | Lazer cutting technology |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive industry | Metals (steel, aluminum) | CO2 & fiber lasers |
| Aerospace | Titanium, composite materials | Fiber lasers |
| Electronics | Semiconductors, plastic | Nd:YAG lasers |
| Medical equipment | Stainless steel, plastic | CO2 & Nd:YAG lasers |
| Jewelry | Precious metals | Fiber lasers |
However, as with any art, there are nuances. For example, microelectronics, biomedicine, or jewelry — these industries have specific requirements that may not be achievable with lazer cutting.
In such cases, specialized methods come to the rescue like fiber laser cutting & electroplating, which, although not as versatile, are target suited to the task at hand.
Nevertheless, ask any laser craftsman, and they will tell you about the thrill of seeing a masterpiece being created from an ordinary sheet of metal.
Finalization
Laser cutting, a technology that already plays a key role in many manufacturing processes on a daily basis, promises to become a key element for testing large projects in the future.
Today, the range of precision-cut applications covers businesses such as drone modeling and mass production of designer accessories and jewelry. From a business point of view, the most promising industries for the application of this technology are automotive, medical devices and musical instruments (Nature.com).
These are the industries whose goods consist of thousands of small parts, requiring jewelry precision in manufacturing. Among the diverse applications of laser cutting, 3D printing and communication technologies stand out.
These fields hold significant business potential. So, if you have a prototype idea that can be brought to life using lazer cutting, here’s what you need to do to enter the market:
- Develop design — create a digital model of the prototype using CAD software, this could be an SVG file for the lazer.
- Select and prepare suitable material for cutting:
- Calibrate the equipment according to the project requirements.
- Actually start the cutting process, during which the laser follows the contours of the model exactly.
- Clean and finalize the parts to a marketable appearance. Next, it’s a matter of marketing strategy.
Despite the obvious advantages, technical and economic obstacles may stand in the way: slow integration of laser cutting into production processes, long supply chains for the necessary materials and competition with large companies.
In addition, the high cost of the equipment and the requirement for specialized knowledge to use it imply a significant investment. Lazer cutting, although similar to 3D printing, is more specialized. It is ideal when these two technologies complement each other.
But, to start somewhere, laser technology is preferable — recommend the experts from Art4youSpace, who every day accept orders for SVG patterns from startups who dare to make a name for themselves. Experts’ predictions indicate that, despite the numerous obstacles, this particular technological advancement will progress rapidly, offering manufacturers fresh chances for ingenuity.

