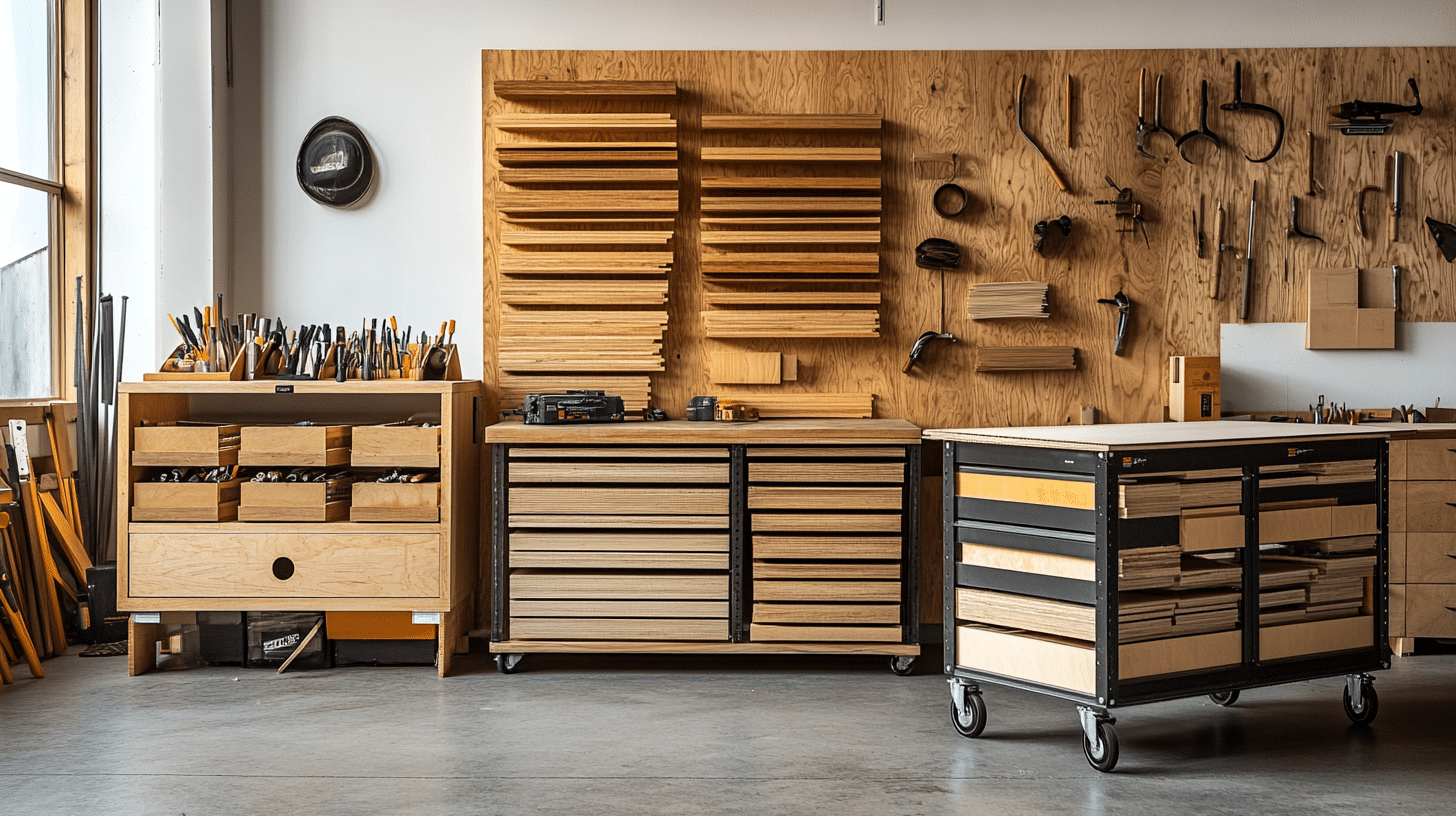
DIY Scrap Wood Storage: Cost-Effective Solutions for Every Workshop
Woodworkers face the inevitable challenge of managing scrap wood accumulation in their workshops.
These valuable remnants from previous projects often create cluttered spaces, making maintaining an efficient and safe working environment difficult.
An effective storage system can transform your workshop into a more productive space while ensuring easy access to these useful materials.
A well-organized scrap wood storage solution offers multiple benefits beyond just tidiness. It helps prevent material waste, improves workshop safety, and enhances overall productivity by making locating and utilizing available resources easier.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through various storage solutions, from simple DIY plans to expert organizational strategies, helping you create a system that perfectly suits your needs.
Understanding Your Scrap Wood Storage Needs
1. Assessing Your Scrap Wood Collection
Understanding your scrap wood inventory is crucial for developing an effective storage solution. Different types of wood, from heavy hardwoods to delicate veneers and sheet goods, require different storage considerations.
Take time to sort through your collection, identifying categories like plywood scraps, hardwood offcuts, and dimensional lumber pieces.
The key to successful storage is recognizing which pieces are worth keeping. Pieces smaller than 10 inches in both dimensions might be better suited for the scrap bin, while larger pieces deserve dedicated storage space.
2. Identifying Space Constraints
Your workshop’s physical limitations are crucial in determining the most suitable storage solutions. To understand your spatial constraints, measure available wall space, ceiling height, and floor area.
When planning storage locations, consider traffic patterns and workflow requirements.
Natural lighting and ventilation should also be considered in your space assessment. Properly placed storage units can help maintain good airflow while maximizing available space.
3. Defining Your Goals
Establishing clear objectives for your storage system helps ensure the final solution meets your specific needs.
Consider factors like accessibility requirements, frequency of use, and whether mobility is essential for your workflow. Your storage goals should align with your working style and project types.
Think about future needs as well as current requirements. A well-planned storage system should be adaptable enough to accommodate changes in your woodworking focus or workshop layout.
Step-By-Step DIY Scrap Wood Storage
STEP 1: Prepare the Lumber
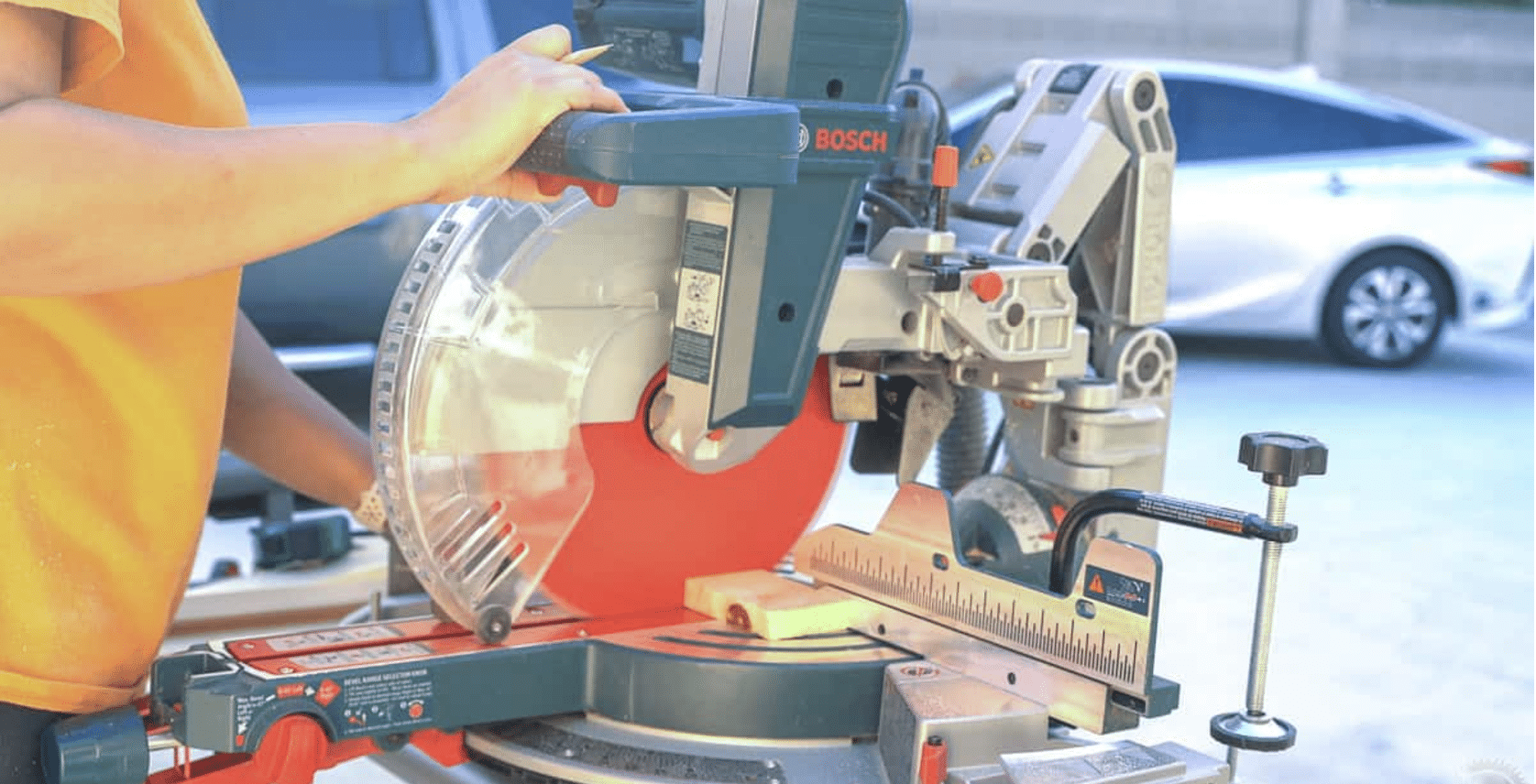
Start by gathering all the boards you need and cutting them according to the list. As I did, you can use scrap wood for this project by cutting it down to the required sizes.
Sanding the boards is optional since this storage cart holds lumber, so smoothness is not a priority.
This step helps ensure you have all the materials ready before assembly.
STEP 2: Make Pocket Holes
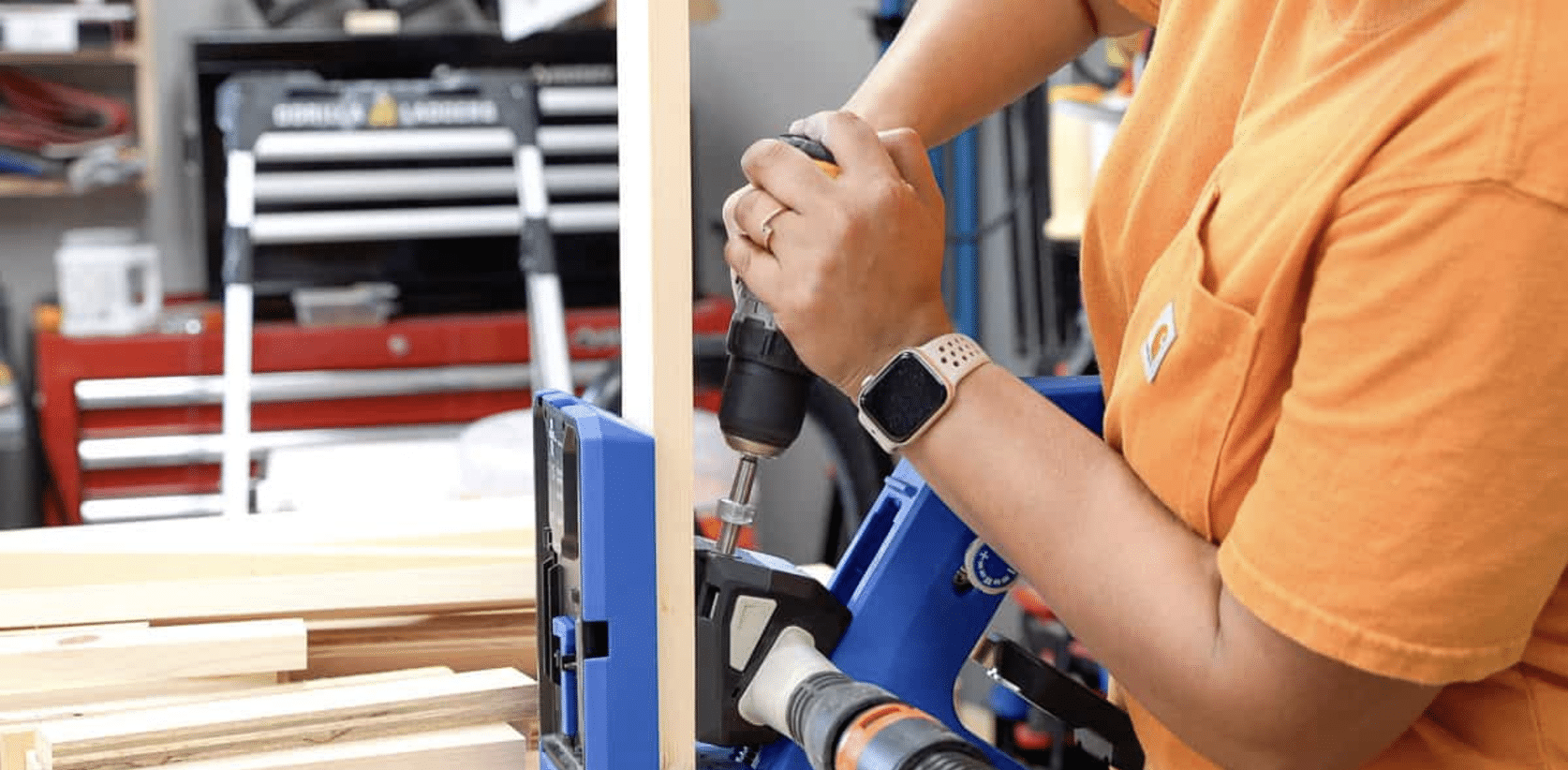
Set up your pocket hole jig to drill holes for ¾-inch material. Pocket holes make assembling the cart quick and sturdy.
I used a Kreg 720, but any jig will work for this. Be sure to periodically check that the jig collar is tight and in the correct position to avoid overly deep holes.
Making these pocket holes is essential for a smooth and efficient assembly process.
STEP 3: Assemble the Frames
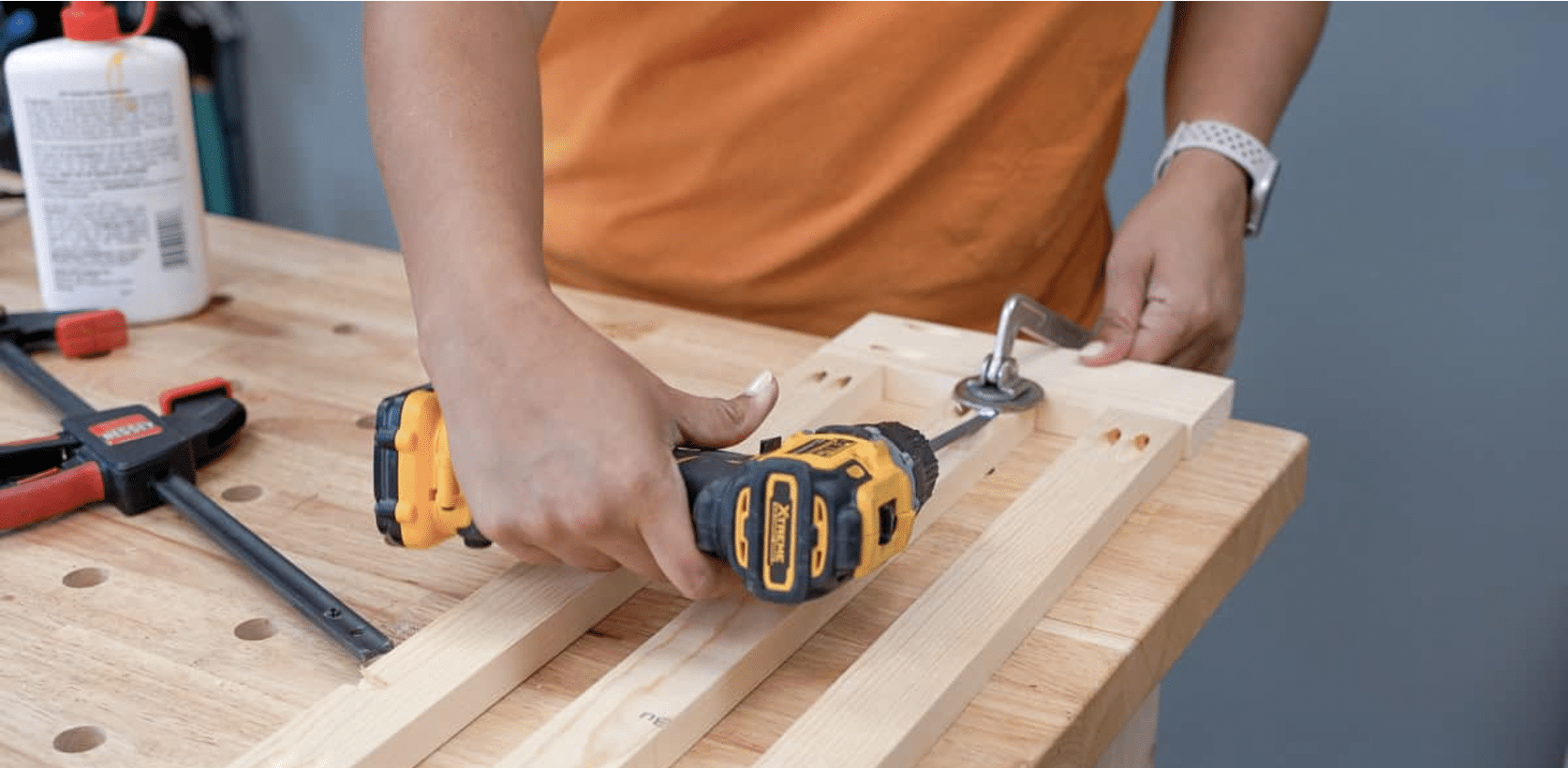

Build the cart by assembling its tiers. Start by creating the front, middle, and back frames. Use wood glue and one ¼-inch pocket hole screws to attach the slats to the frame sides.
Clamps, such as face or F-style bar clamps, will help align and stabilize the boards while you secure them.
Attach dividers to the slats on the front and middle frames, ensuring everything is aligned for stability.
STEP 4: Attach the Frames to Build the Cart
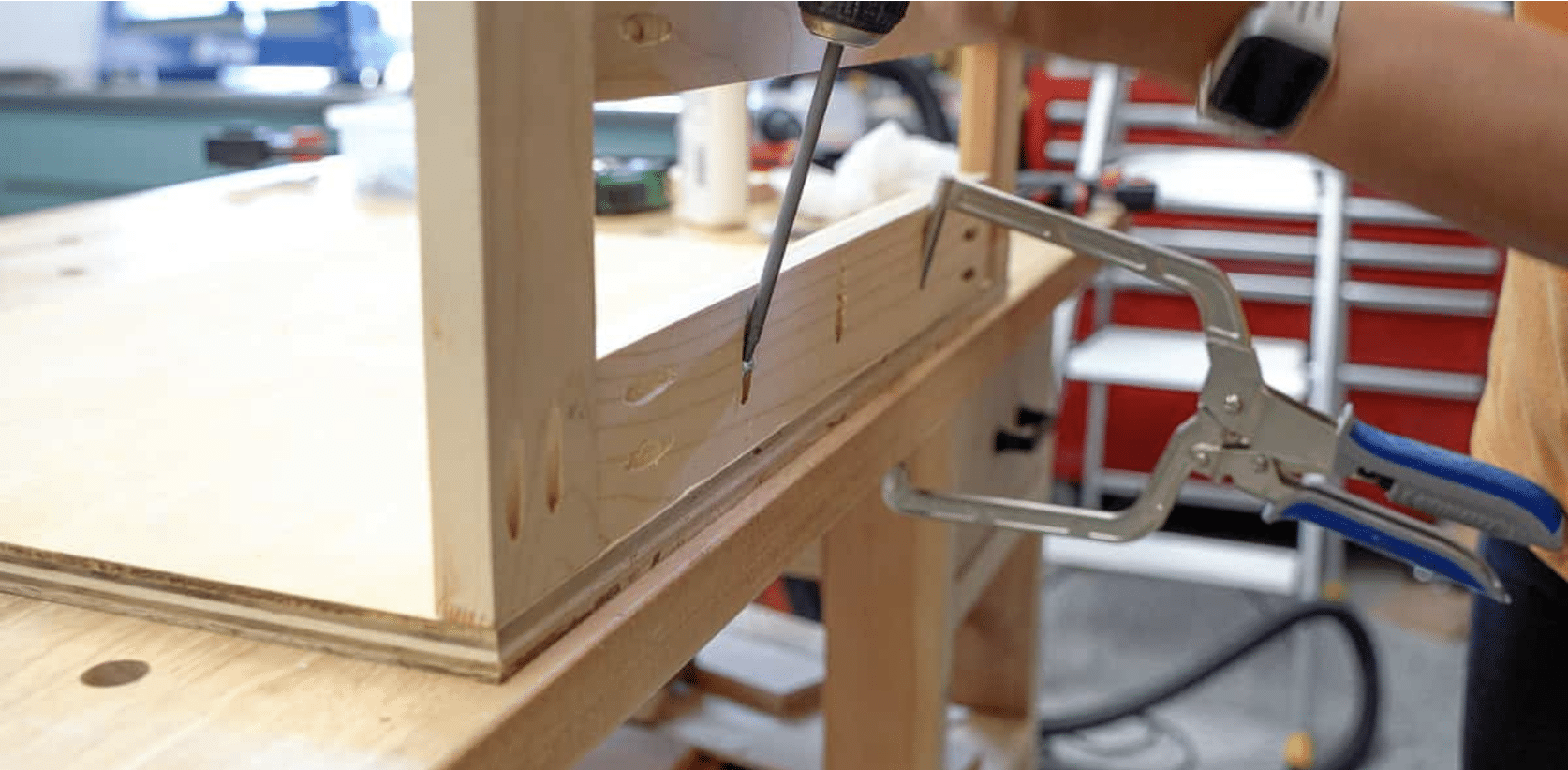
Attach the frames to the base plywood, starting with the back frame. Secure it with pocket hole screws, using a right-angle clamp to keep it in place.
Next, attach the middle frame to the base and connect the dividers to the slats on the previous frame.
Finally, the front frame is attached using the same method. A right-angle drill attachment can help you access tight spots during this step.
STEP 5: Add the Casters
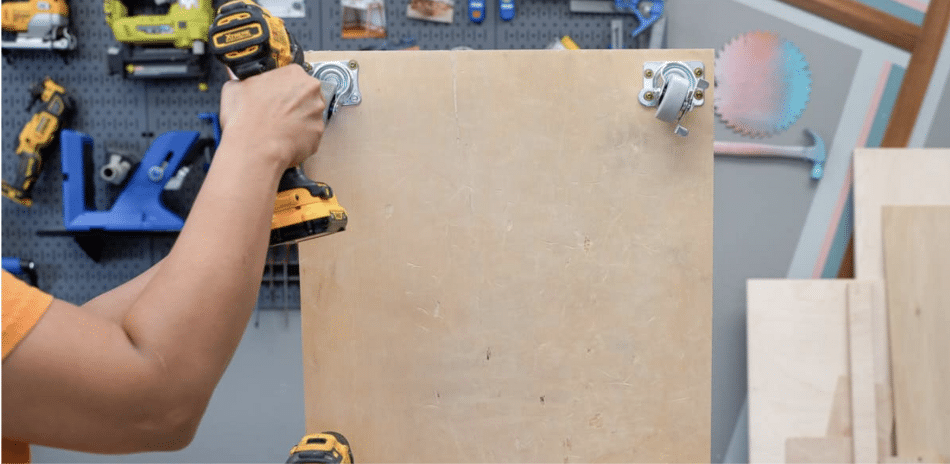

Attach 2-inch casters to the bottom of the base plywood to make the cart mobile. Use screws to secure the casters, ensuring they are strong enough to hold the cart and its contents.
If the screws are slightly long, add washers to adjust the fit. Casters are a practical addition, allowing you to move the cart around your workspace as needed easily.
Video Tutorial
For more details, check out this video tutorial by Shara Woodshop Diaries.
Exploring Scrap Wood Storage Options

1. Stationary vs. Mobile Storage Solutions
Fixed storage systems offer stability and maximum capacity utilization. These permanent installations work well for workshops with established workflows and dedicated zones.
Wall-mounted systems and built-in shelving units provide reliable storage without consuming valuable floor space.
Mobile storage solutions offer flexibility and convenience, particularly in smaller workshops. Rolling carts and portable bins allow you to move materials exactly where needed, adapting to different project requirements and workspace configurations.
2. Vertical and Horizontal Storage Ideas
Vertical storage maximizes wall space utilization while keeping materials easily accessible. Wall-mounted racks with adjustable dividers effectively accommodate different sizes of scrap wood.
Pegboard systems offer customizable storage options that can evolve with your needs.
Horizontal storage solutions work well for larger sheet goods and longer pieces. Floor-based bins and stacking systems can efficiently organize materials while easily accessing frequently used pieces.
3. Creative and Space-Saving Designs
Overhead storage systems tap into often-overlooked space near the ceiling. Retractable pulley systems and ceiling-mounted racks can store longer pieces or less frequently used materials safely out of the way.
Fold-away storage units provide flexible solutions for tight spaces. These systems can be expanded and tucked away to free up workspace during projects.
4. Multi-Functional Storage Solutions
Integrating storage into existing workshop fixtures maximizes space efficiency. Workbenches with built-in storage compartments serve double duty, while mobile bases can transform stationary storage into flexible solutions.
Consider incorporating storage into other workshop elements like assembly tables or outfeed supports. This approach helps maintain workshop flow while providing additional organization options.
Organizing and Maintaining Your Scrap Wood Inventory
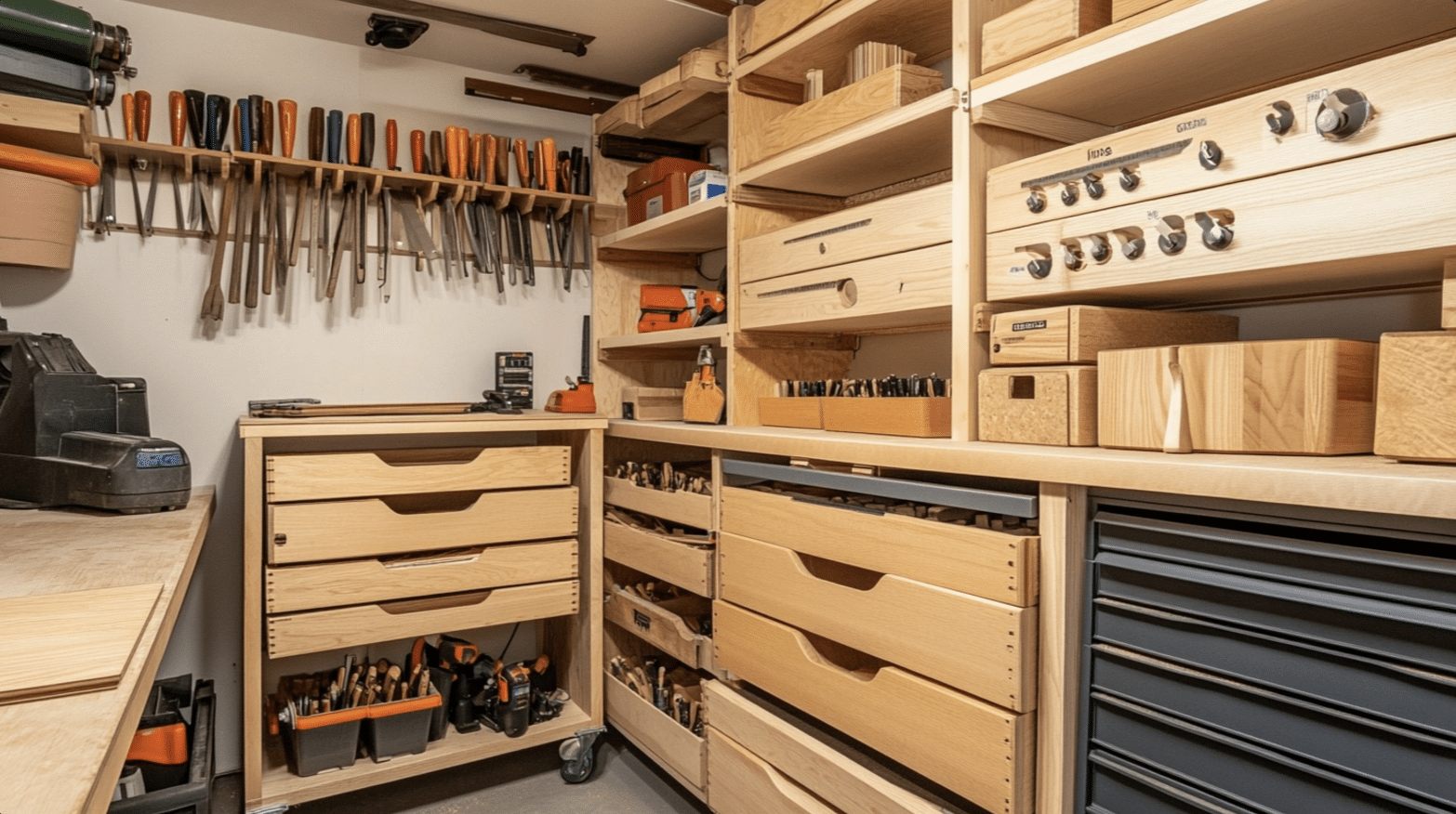

Effective Categorization Methods
A systematic approach to categorizing scrap wood makes retrieval and organization significantly easier.
Create distinct zones for different materials, such as hardwoods, softwoods, plywood scraps, and specialty woods. This natural grouping system helps you quickly locate the right piece for your next project.
Consider implementing a size-based organization system within each category. Larger panels and longboards can be stored vertically, while smaller pieces might work better in labeled bins or drawers.
Inventory Management Tools
Digital tools can streamline your scrap wood inventory management process. A simple spreadsheet tracking system can help monitor your available materials, their dimensions, and potential project applications.
Mobile apps for workshop organizations offer features like photo documentation and quick search capabilities.
Regular inventory updates ensure your tracking system remains useful. Document new additions and remove used pieces from your inventory list to maintain accuracy.
Best Practices for Maintenance
Establish a routine maintenance schedule for your storage system. Monthly reviews help identify unused materials and reorganize spaces that may have become cluttered during busy project periods.
Consider implementing a “one-in-one-out” rule to prevent overflow. When adding new scrap pieces, evaluate existing materials to maintain manageable inventory levels.
Safety Considerations in Scrap Wood Storage
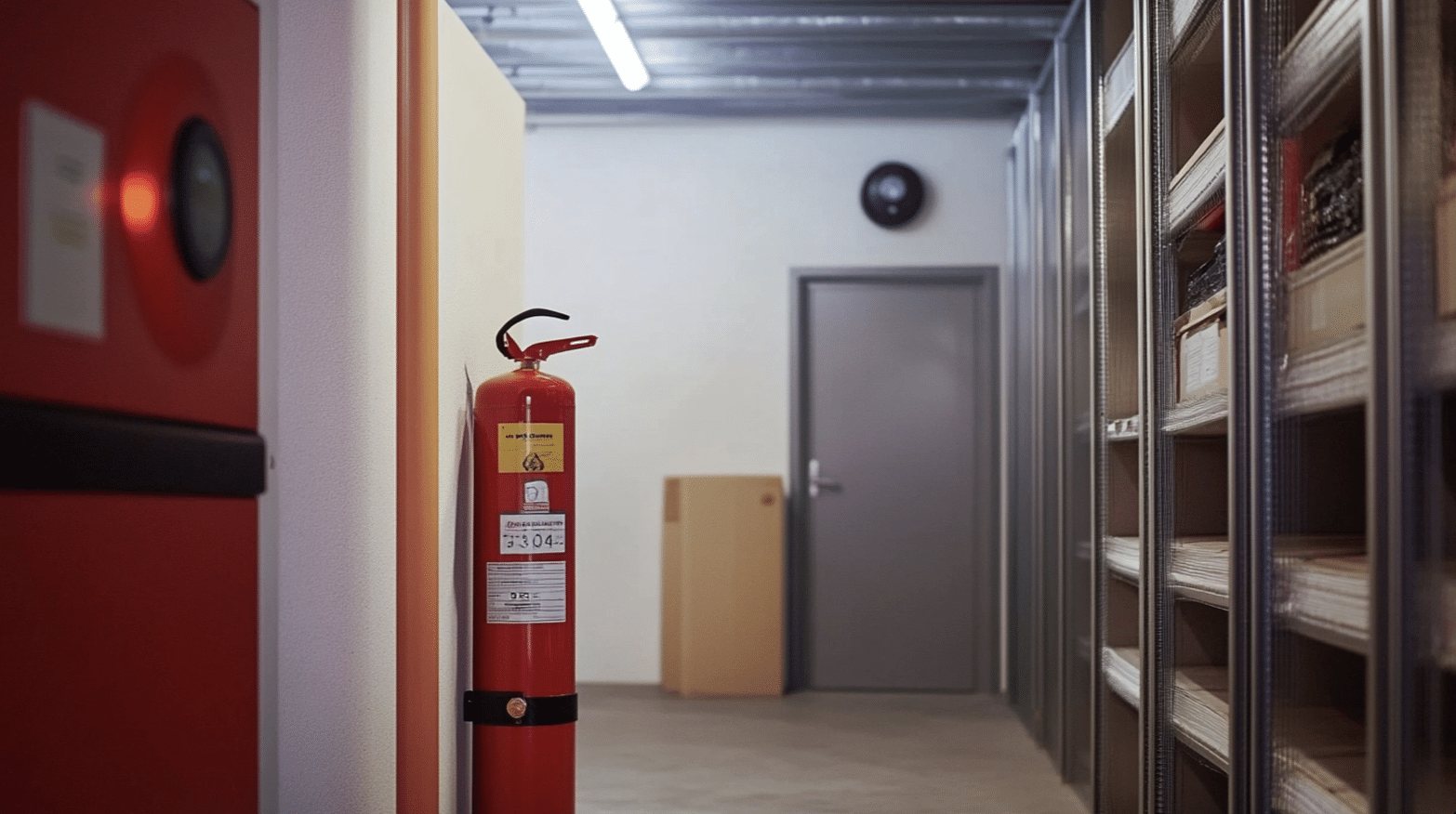

1. Proper Weight Distribution and Structural Integrity
Storage units must be designed to handle the substantial weight of accumulated wood scraps. Ensure wall-mounted systems are properly anchored into studs and floor-based units have adequate support structures.
Regular inspections of storage components help identify potential weaknesses before they become hazards. Pay special attention to weight-bearing joints and mounting points under heavy load.
2. Preventing Fire Hazards
Wood storage requires careful consideration of fire safety. Proper spacing between storage units and heat sources, including electrical equipment and heating systems, is essential.
Good airflow around stored materials helps prevent moisture accumulation and reduces fire risk.
Install smoke detectors near storage areas and keep fire extinguishers readily accessible. Regular cleaning to remove wood dust and debris further minimizes fire hazards.
3. Handling and Storing Treated Wood
Due to its chemical content, treated lumber requires special storage considerations. To prevent chemical transfer, store pressure-treated materials separately from regular scrap wood.
Ensure adequate ventilation around treated wood storage areas.
Use appropriate personal protective equipment when handling treated materials. Consider storing these materials in dedicated containers or on separate shelving units.
4. Pest Prevention
Protect your valuable wood scraps from pest infestation through preventive measures. High storage solutions keep materials off the floor, reducing the risk of moisture damage and pest access.
Regular inspections help identify potential pest problems early.
The application of appropriate wood sealants can provide additional protection. In storage areas, consider using cedar blocks or other natural pest deterrents.
Maximizing Small Workshop Spaces
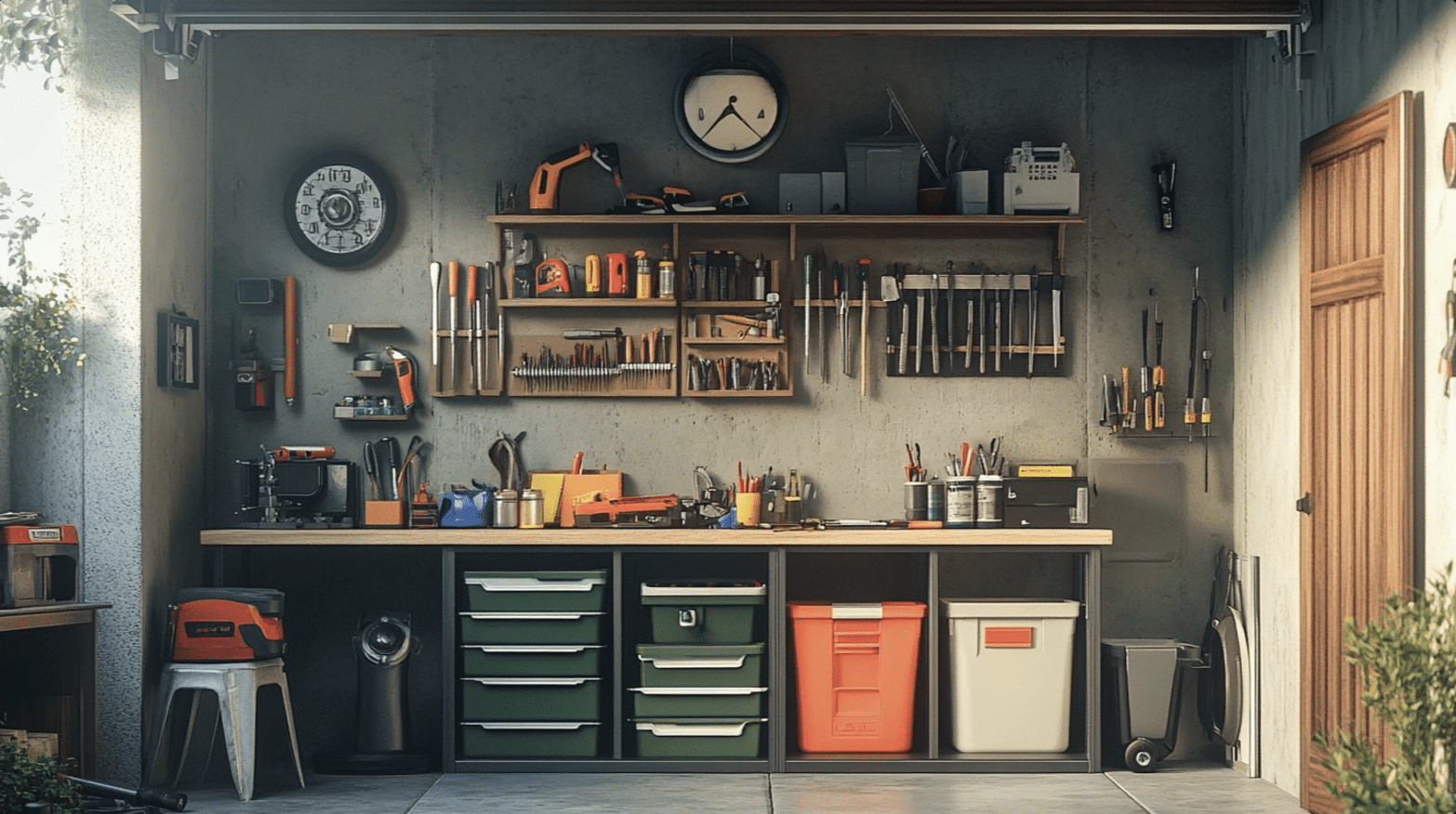

Utilizing Underused Areas
Small workshops demand creative storage solutions. Use pull-out bins or sliding shelves to transform the space under workbenches into organized storage.
Overhead areas above doors and windows offer excellent opportunities for additional storage capacity.
Corner spaces, often overlooked, can become valuable storage areas with properly designed units. Custom-built corner shelving maximizes these traditionally difficult-to-use spaces.
Space-Efficient Design Tips
Implement modular storage solutions that can adapt to changing needs. Sliding storage panels mounted on wall tracks provide access to materials while maintaining a small footprint. Fold-down workstations with integrated storage optimize space usage during different activities.
Consider multi-level storage systems that take advantage of vertical space. Mobile storage units that nest together when not in use offer flexibility without permanently consuming floor space.
Improving Workshop Efficiency
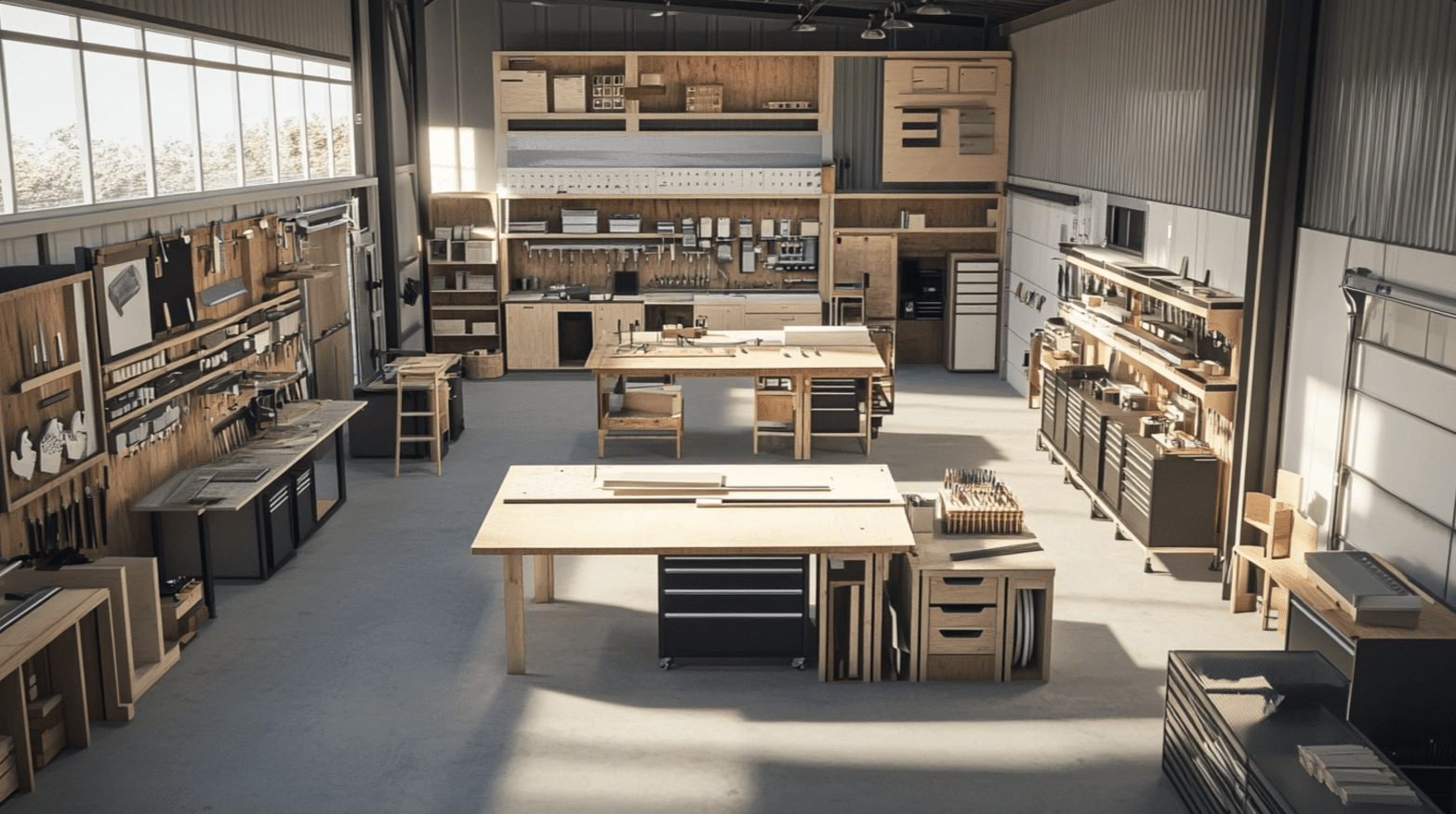

Workflow Optimization
Arrange your storage systems to support natural workflow patterns. Position frequently used materials within easy reach of primary work areas.
Create dedicated zones for different activities, with appropriate storage solutions supporting each area.
Consider the relationship between material storage and waste management. Positioning scrap storage near cutting stations reduces walking distance and improves efficiency. AI is also a powerful tool for assessing workshop waste, with many waste managementcompanies already utilizing it. Waste Direct, a proponent of AI-driven workflows, reports that AI can enhance sorting systems, improving recycling efficiency.
Blending Tool and Material Storage
Combine tool storage with material organization for improved workflow—design storage units that accommodate tools and related materials, keeping everything needed for common tasks within reach.
Implement modular systems that can adapt to changing tool collections and material needs. Mobile storage units can keep tools and materials together for specific projects.
Expenses and Cost Considerations
| CATEGORY | PRICE RANGE | DETAILS |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Basic DIY Storage Solutions | $50-$150 | 2x4s ($4-$6 each), plywood sheets ($30-$45 per sheet), basic hardware ($20-$50 additional), and caster wheels ($8-$15 each). |
| 2. Mid-Range Storage Options | $150-$500 | Heavy-duty casters ($20-$30 each), high-grade plywood ($60-$80 per sheet), quality hardwood ($4-$8 per board foot), drawer slides ($15-$30 per pair), brackets ($8-$15 each), professional-grade hardware ($50-$100), finishing materials ($30-$50). |
| 3. Premium Storage Systems | $500-$1,500+ | Industrial-grade casters ($40-$60 each), premium hardwood ($200-$400), professional-grade drawer systems ($100-$200), automated lift systems ($200-$500), custom hardware and accessories ($150-$300). |
Money-Saving Strategies
Significant savings can be achieved through careful planning and material sourcing. Watch for lumber yard sales, where 20-40% savings are common. Building during off-peak seasons (typically winter) often yields better material prices.
Consider phased implementation to spread costs over time. Start with essential storage components ($100-$200) and expand as budget allows.
Many woodworkers successfully begin with a basic mobile cart ($75-$125) and add specialized storage solutions as their needs evolve.
Conclusion
Effective scrap wood storage is fundamental to maintaining a productive and enjoyable workshop environment.
Implementing these organizational strategies and solutions can create a more efficient workspace that supports your woodworking goals.
Take the first step today by evaluating your storage needs and beginning with simple improvements.
Remember that the perfect storage system evolves with your workshop and working style. Stay flexible in your approach and be willing to adapt your storage solutions as your needs change.
Share your successful storage ideas with fellow woodworkers and continue learning from the community’s collective experience.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How Do You Best Store Scrap Wood?
Organize scrap wood by type and size using vertical racks, wall-mounted systems, or mobile carts. Keep frequently used pieces accessible and ensure proper ventilation to prevent damage.
How Do You Get Rid Of A Lot Of Scrap Wood?
Scrap wood can be disposed of responsibly through recycling centers, donated to usable pieces to local schools or workshops, or repurposed for DIY projects and home improvement tasks.
How Do You Store Large Amounts Of Wood?
Store large wood quantities in dry, ventilated areas using horizontal racks or stacking systems. Utilize wall-mounted or overhead storage to maximize space and keep materials organized.